Database Fundamentals
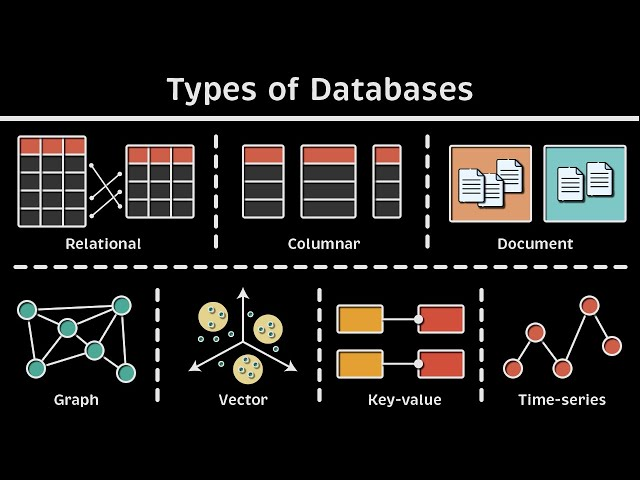
Database Family: Types and Use Cases
you need to know how to use the database for webdevelopment and data storage is the base of the whole development.
1. Relational Database (RDBMS)
Definition: Stores data in structured tables with rows/columns and enforces relationships via keys.
Key Features:
- ACID compliance (Atomicity, Consistency, Isolation, Durability)
- SQL query language
- Schema-defined structure
Popular Systems: - PostgreSQL, MySQL, SQLite
When to Use: - Financial transactions
- Applications requiring strict data integrity
2. PostgreSQL
Why Stand Out?
- Advanced JSON support
- Full-text search
- Geospatial data handling
Example SQL:
-- Create a user table
CREATE TABLE users (
id SERIAL PRIMARY KEY,
name VARCHAR(50) NOT NULL,
email VARCHAR(100) UNIQUE
);
3. SQL (Structured Query Language)
Core Operations:
SELECT * FROM products WHERE price > 100; -- Query data
INSERT INTO orders (user_id, total) VALUES (1, 99.99); -- Insert data
UPDATE users SET status = 'active' WHERE id = 5; -- Modify data
Other database types
1. Graph Database
Definition: Uses nodes/edges to represent relationships (e.g., social networks).
Key Features:
- Optimized for relationship-heavy queries
- Flexible schema
Tools: - Neo4j, Amazon Neptune
Use Case:
// Find friends of a user in Neo4j
MATCH (u:User {name: "Alice"})-[:FRIEND]->(friend)
RETURN friend.name;
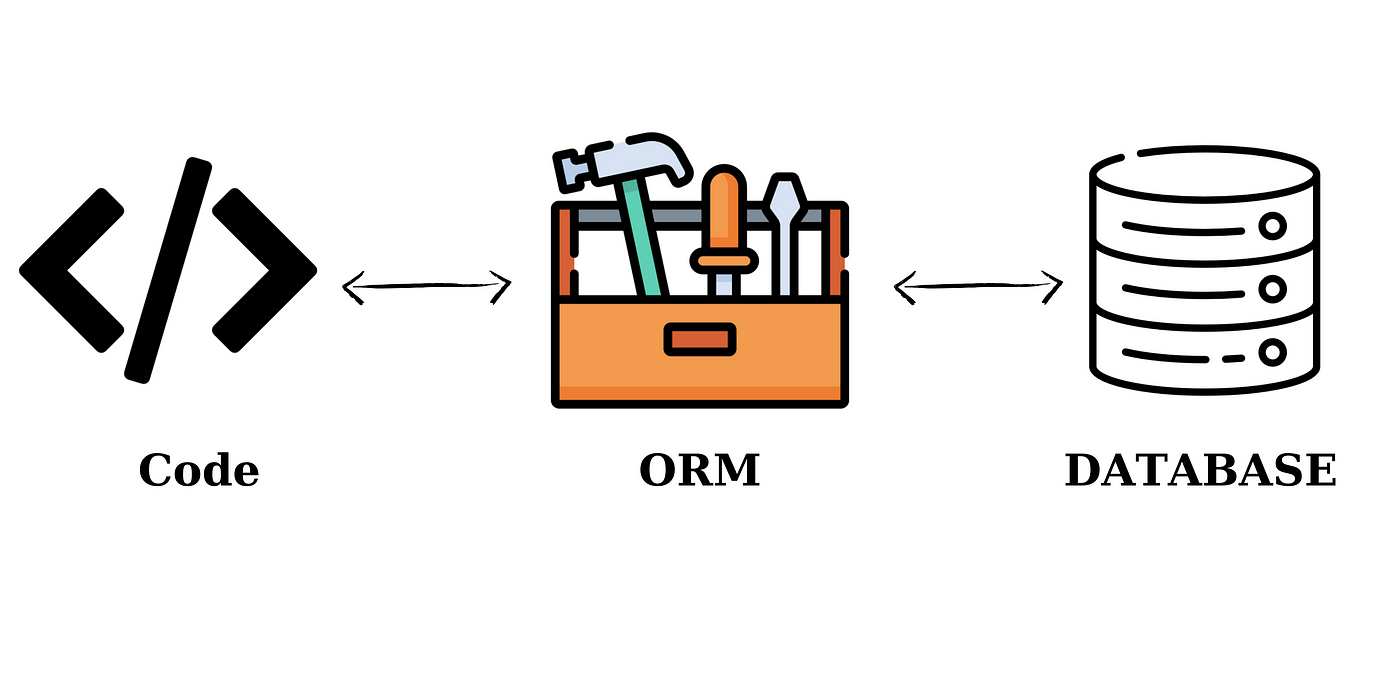
ORM: Bridging Code and Databases
What is ORM?
Object-Relational Mapping converts database tables into code objects (e.g., JavaScript/Java classes).
1. Doctrine with Symfony (PHP)
Setup:
composer require doctrine/orm
Entity Example:
// src/Entity/Product.php
namespace App\Entity;
use Doctrine\ORM\Mapping as ORM;
#[ORM\Entity]
class Product {
#[ORM\Id]
#[ORM\GeneratedValue]
private ?int $id = null;
#[ORM\Column(type: 'string')]
private string $name;
}
2. Node.js ORM Tools
Popular Libraries:
- Sequelize (Supports PostgreSQL/MySQL):
const { Sequelize, Model } = require('sequelize');
const sequelize = new Sequelize('postgres://user:pass@localhost:5432/dbname');
class User extends Model {}
User.init({ name: Sequelize.STRING }, { sequelize }); - TypeORM (TypeScript-friendly):
import { Entity, PrimaryGeneratedColumn, Column } from "typeorm";
@Entity()
export class User {
@PrimaryGeneratedColumn()
id: number;
@Column()
name: string;
}
Pro Tip
When to Use What?
| Scenario | Tool Recommendation |
|---|---|
| Strict data relationships | PostgreSQL + TypeORM |
| Rapid prototyping | SQLite + Sequelize |
| Social network features | Neo4j (Graph Database) |
Learning Resources
Tools
- Datagrip: use the database in one platform
- Prisma: